Brief Introduction about the Yoruba People
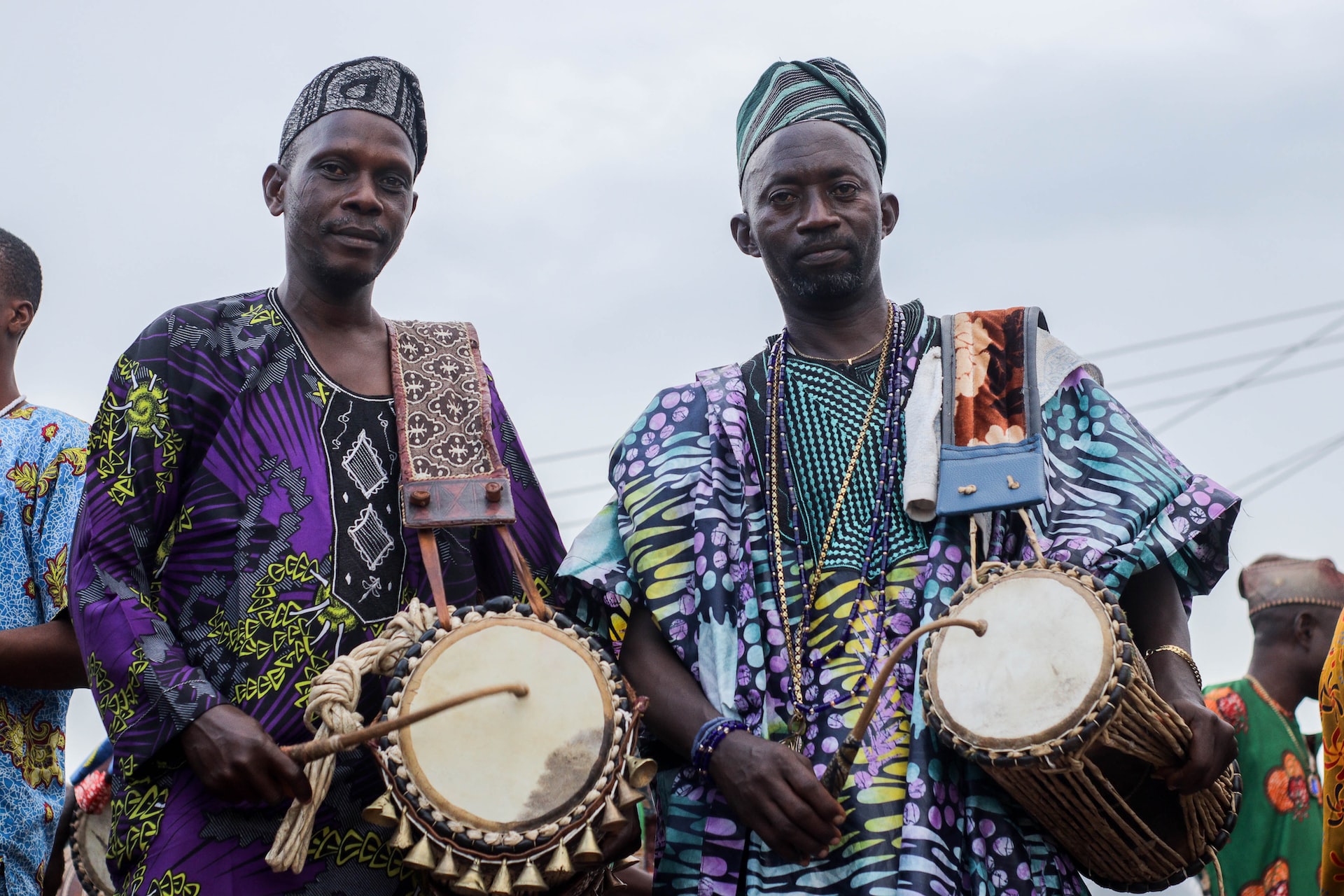
The Yoruba people, originating from West Africa, primarily Nigeria, Benin, and Togo, boast a rich cultural heritage with a history spanning centuries. Their tradition of oral history forms the cornerstone of their early narrative, passed down through generations. According to these tales, their migration from the Middle East to West Africa occurred over 1,000 years ago, led by the warrior Oduduwa, who emerged as their inaugural king.
With time, the Yoruba community evolved a sophisticated governance system, where individual city-states were ruled by kings (oba). These states often engaged in both conflict and trade, fostering cultural exchange. Despite involvement in the transatlantic slave trade during the 19th century, with many falling victim to European traders, resistance also emerged. Figures like the warrior queen Efunroye Tinubu actively opposed the trade.
In the 20th century, the Yoruba people increasingly engaged in politics, playing a pivotal role in Nigeria’s struggle for independence. Today, they diligently preserve their cultural traditions, contributing significantly to Nigerian and African culture, music, and literature.